Alcohol dehydrogenase monomer
sketchfab
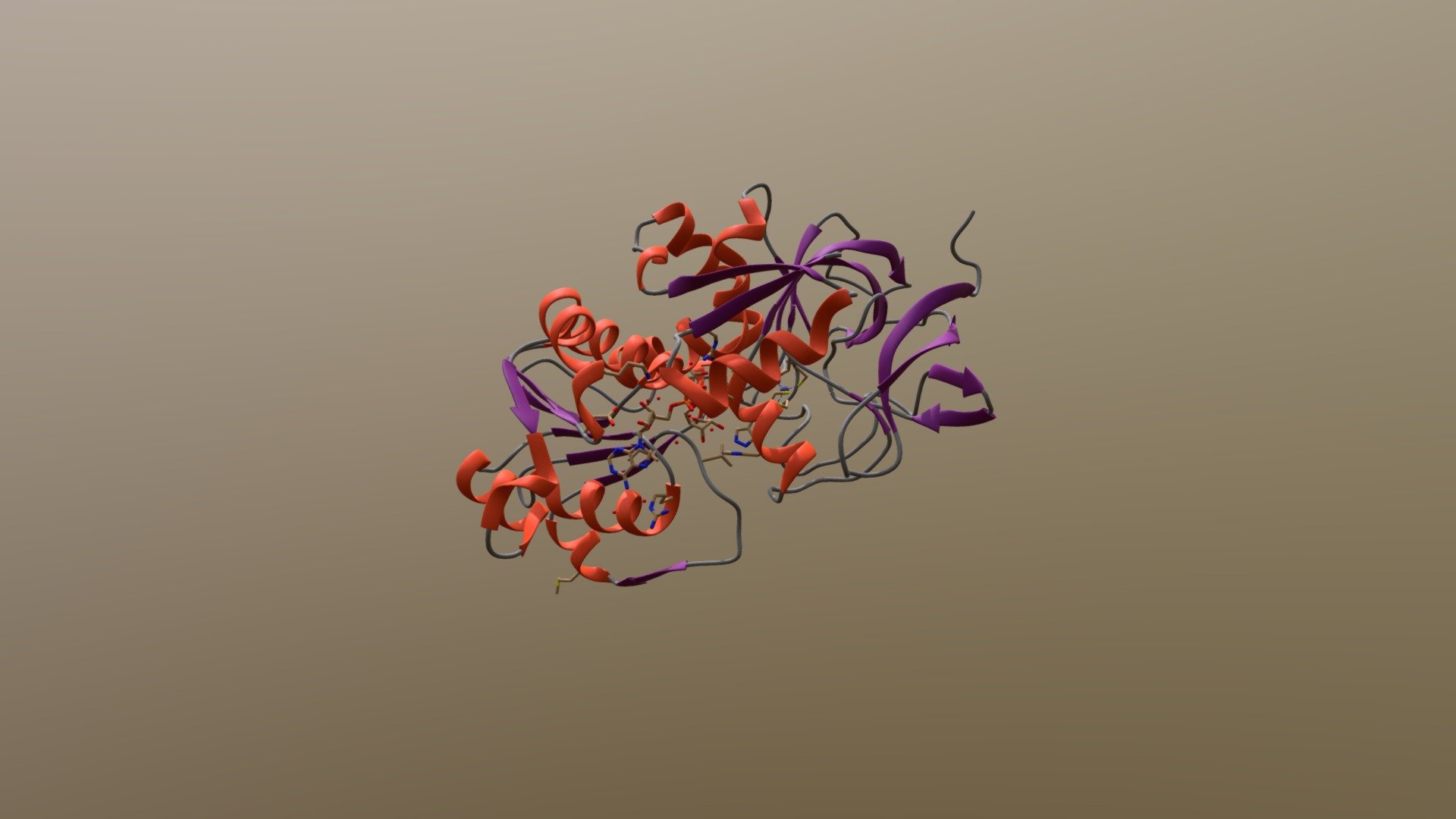
Human alcohol dehydrogenase. ADH is a homodimer. Each monomer has 374 residues with molecular weight of 74000 dalton. There are two domains. The NAD+-binding domain (residues 176-318) is a central beta-sheet of 6 strands flanked by alpha helices. NAD+ binds to the C-terminus of the beta-sheet. The catalytic domain (residues 1-175, 319-374) also has a alpha/beta structure. The inter-domain interface forms a cleft which contains the active catalytic site. The interface is formed by two helices, one from each domain crossing over each other. There are two Zn++ cations per monomer, one at the catalytic site being mandatory for catalysis. The alcohol substrate binds inside the cleft where the Zn++ cation is, whilst the nicotinamide ring of the NAD finds its way pointing into the cleft. The dimer forms with the two NAD-binding domains packing together such that their 2 central beta sheets combine to form a 12-stranded beta sheet. The catalytic domains are situated at opposite ends.
With this file you will be able to print Alcohol dehydrogenase monomer with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on Alcohol dehydrogenase monomer.
