Dice probability
thingiverse
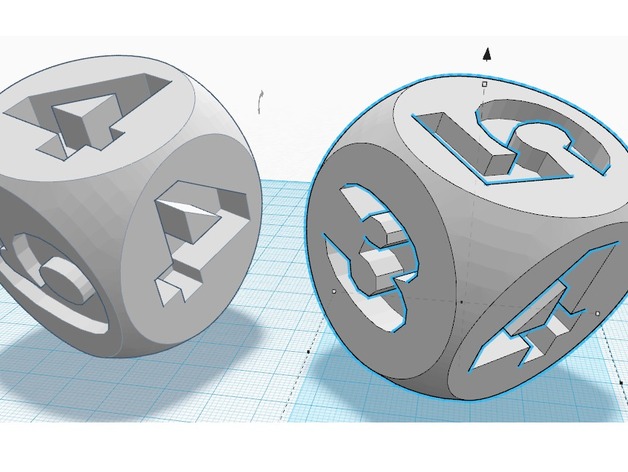
Students are required to create two dice, one balanced and one unbalanced. When the dice are printed, students will then perform an experiment in which they roll the dice separately a certain amount of times and keep a tally chart of numbers that appear. Students then compare the theoretical and experimental probabilities and draw a conclusion at the end. How I Set This Up Step 1 Go to symbols tab and click on "DICE". Drag the item to the center of the grid Step 2 You will make a die with numbers 1-6. This will be the balanced die. Make sure you make the numbers mesh with the die block, click on hole button, Then click the group button to make sure the number has been indented into the die. Step 3 You will make a second die. This die will be unbalanced so make sure you have numbers that repeat on the faces of the die. You will follow the same procedure as step 2!!! "Project: What are the Odds?" Overview and Background 1) Students will need to figure out theoretical probabilities using both balanced and unbalanced dice. Examples will include: probability of one number on a balanced die, probability of one number on an unbalanced die, and probability of an even number or odd number. 2) Students will also compare and contrast theoretical probabilities with experimental probabilities. Objectives Students will be able to: Define theoretical probability Define experimental probability Compare and contrast theoretical and experimental probabilities Apply theoretical and experimental probabilities Audiences This thing is set for grades 7-8 Subjects Mathematics Probability Skills learned CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.5 Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.6 Approximate the probability of a chance event by collecting data on the chance process that produces it and observing its long-run relative frequency, and predict the approximate relative frequency given the probability. For example, when rolling a number cube 600 times, predict that a 3 or 6 would be rolled roughly 200 times, but probably not exactly 200 times. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7 Develop a probability model and use it to find probabilities of events. Compare probabilities from a model to observed frequencies; if the agreement is not good, explain possible sources of the discrepancy. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7.A Develop a uniform probability model by assigning equal probability to all outcomes, and use the model to determine probabilities of events. For example, if a student is selected at random from a class, find the probability that Jane will be selected and the probability that a girl will be selected. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7.B Develop a probability model (which may not be uniform) by observing frequencies in data generated from a chance process. For example, find the approximate probability that a spinning penny will land heads up or that a tossed paper cup will land open-end down. Do the outcomes for the spinning penny appear to be equally likely based on the observed frequencies? Lesson/Activity Step 1) Students will be asked to find a theoretical probability of an event using their dice. Step 2) Students will then roll their Dice a certain number of times and keep a tally of how many times a number has appeared. Step 3) students will then answer questions about their comparison of the probabilities Duration This project will be approximately 30 minutes long Preparation Students should know the definition and application to theoretical and experimental probabilities Students should know how to find the probability of an event. Students will need a balanced die Students will need an unbalanced die
With this file you will be able to print Dice probability with your 3D printer. Click on the button and save the file on your computer to work, edit or customize your design. You can also find more 3D designs for printers on Dice probability.
